Ammonia Heat Pumps
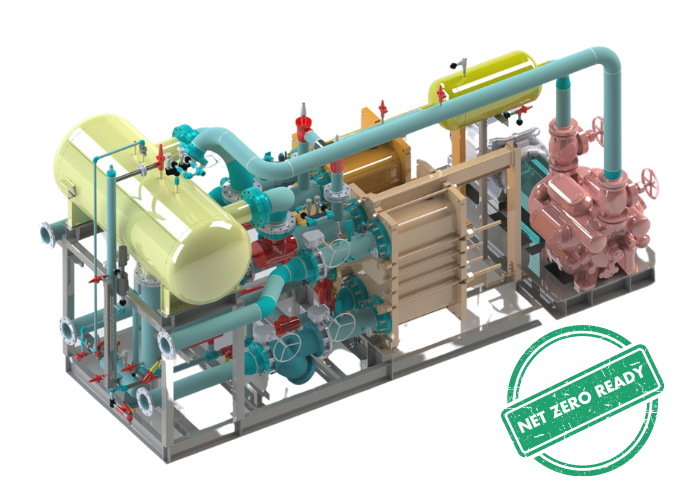
With ever-improving components and technical know-how, industrial ammonia heat pumps can now capture waste heat to deliver heat up to 185°F, making the equipment suitable for use in various applications - like Food and Beverage, District Heating and Cooling, Data Centers, Universities, Health Care Campuses and more.
Ammonia (R717/NH3) is an environmentally friendly refrigerant with zero Ozone Depletion Potential (ODP) and a Global Warming Potential (GWP) of 0. It has been used in large-scale refrigeration and industrial plants for over a century, and its benefits extend beyond environmental gains to include stable pricing and widespread adoption in North America, making the addition of an ammonia heat pump an easy integration.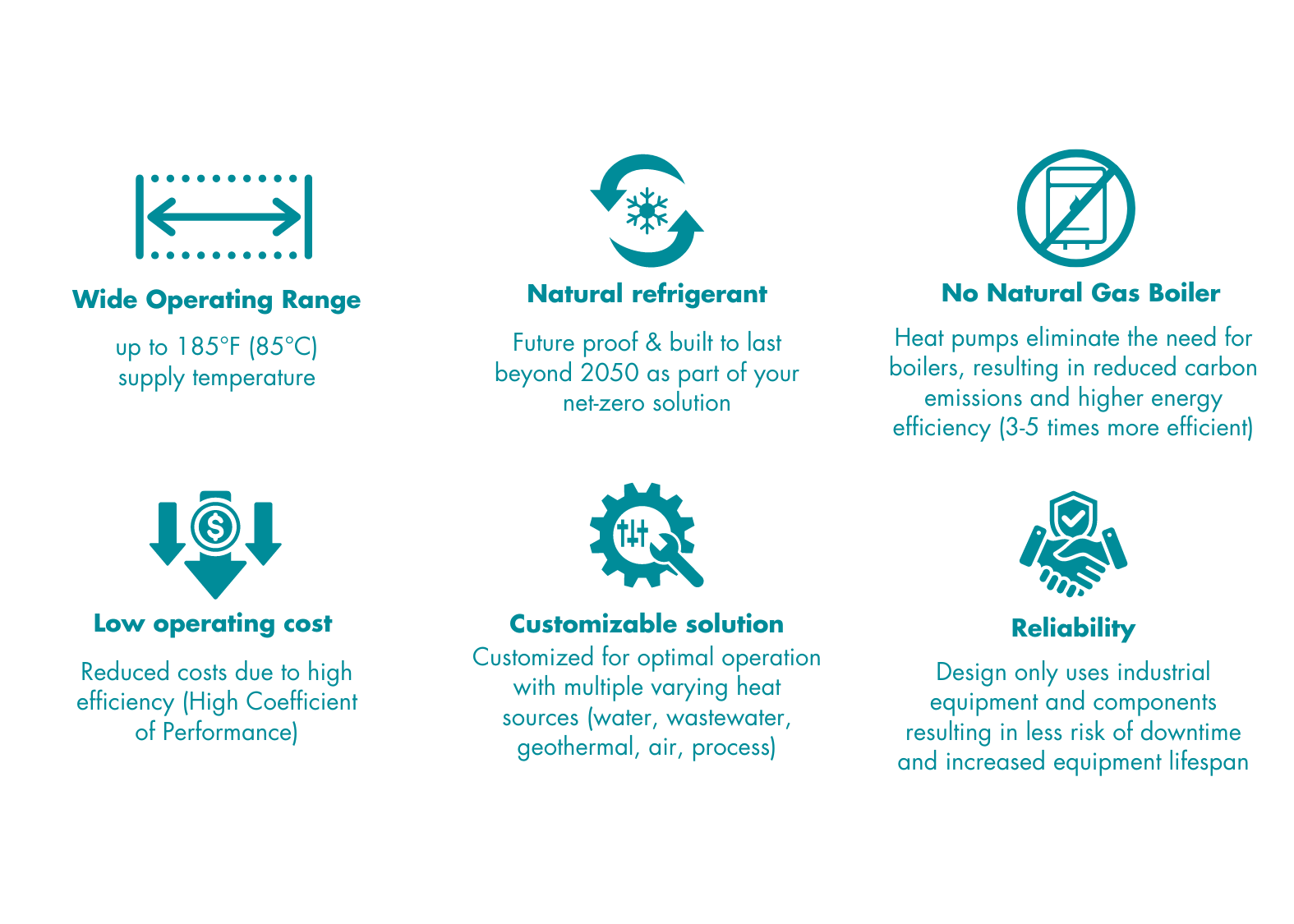

How do heat pumps work?
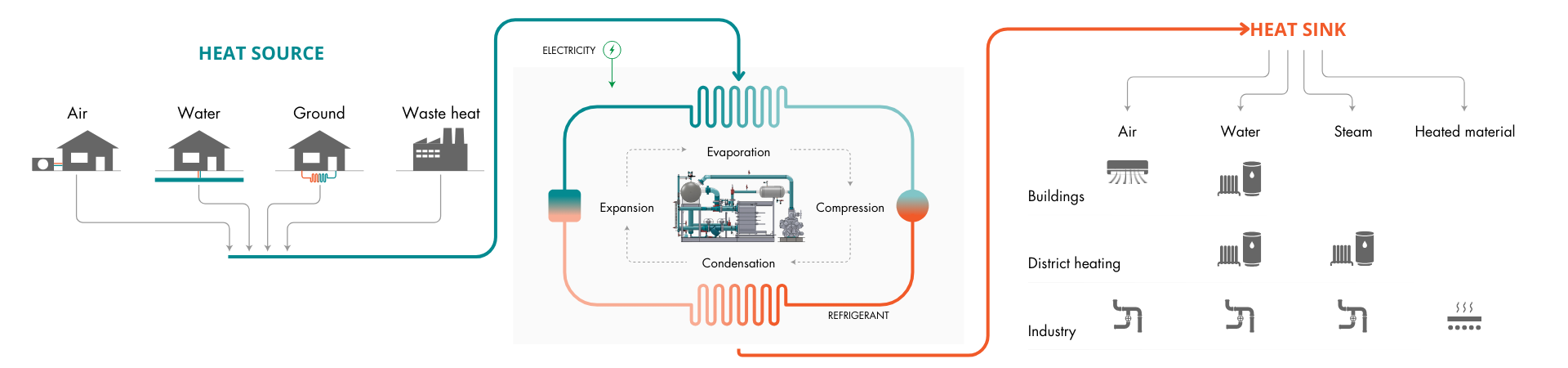
A heat pump works by using the same technology refrigerators or air conditioners use.
It draws heat from various sources (such as air, water, ground, or waste heat from industrial processes) and then amplifies and transfers it to where it's needed. This method of transferring heat, rather than generating it, makes heat pumps notably more efficient than traditional heating methods like boilers or electric heaters, often resulting in lower operational costs
The energy output (heat) from a heat pump is typically several times greater than the energy input required to power it (usually sourced from electricity). Coefficient of Performance (COP) serves as a metric for gauging the efficiency of heat pumps. Industrial heat pump usually have a COP of 3 meaning that for every unit of energy consumed by the heat pump, it produces three units of heat. In other words, it operates at 300% efficiency. This remarkable efficiency allows heat pumps to provide effective heating or cooling while minimizing energy consumption.
Benefits of heat pumps
.png?sfvrsn=d836db22_0)
High Efficiencies
Efficient industrial heat pumps can achieve COP values exceeding 3, especially when using waste heat as a heat source. A heat pump with a higher COP achieves a faster ROI because it provides efficient heating or cooling while minimizing operational expenses.
-(1).png?sfvrsn=8a36db22_1)
Energy Savings
Heat pumps reduce overall energy use due to high thermal efficiencies, especially for low-temperature heating applications and when waste heat sources can be upgraded.
Reliable and Scalable
Heat pumps offer scalable technology, ensuring enhanced supply security, unlike natural gas boilers prone to cost escalation and supply constraints.

Emissions Reduction
By utilizing waste heat and operating efficiently, industrial heat pumps help reduce greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to environmental sustainability and regulatory compliance.
Industry Applications
Related Posts

Industrial Heat Pumps are the Past, Present and Future

Interconnected Efficiency: Leveraging Ammonia Heat Pumps for Sustainable Manufacturing



.png?sfvrsn=5a0ddb22_2)


.png?sfvrsn=8164db22_0)